
For anyone with breathing difficulties, bronchiectasis and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) may seem similar. Both conditions affect your ability to release air from the lungs, causing symptoms like cough, wheezing, and shortness of breath to develop (and worsen).
It’s also not unusual to experience an overlap of bronchiectasis and COPD symptoms. Although differentiating between the two can be challenging, certain factors can help distinguish one from the other.
Is Bronchiectasis COPD?
No. They are two different chronic lung conditions. Bronchiectasis (brong-kee-EK-tuh-sis) is an irreversible condition characterized by the widening and scarring of the airways, leading to excessive mucus production and recurrent infections.¹
What Is COPD?
COPD is an umbrella term used to describe other impaired breathing conditions, including
- Emphysema
- Chronic bronchitis
COPD is categorized by the narrowing of the airways and an obstructed airflow.²
Bronchiectasis and COPD: Understanding the Key Differences
In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between bronchiectasis and COPD, including their causes, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. By the end, you’ll understand how to differentiate between these two conditions and how to seek appropriate medical care.
Causes
Bronchiectasis can be caused by various factors, including genetic conditions, immune system disorders, or respiratory infections,³ whereas COPD is primarily caused by external factors, such as smoking or exposure to lung irritants.4
Another difference between bronchiectasis and COPD is the pattern of lung damage. In bronchiectasis, the airways become widened and scarred, producing excessive mucus and recurring infections.

In contrast, COPD primarily involves narrowing the airways and destroying the air sacs in the lungs, resulting in reduced lung function and airflow obstruction.
Diagnosis
To differentiate between bronchiectasis vs. COPD, healthcare professionals employ various diagnostic tests. These tests help determine the underlying cause and identify the specific condition affecting your respiratory health.
- With COPD, for example, imaging tests, such as chest X-rays or CT (computerized tomography) scans5 provide detailed images of the airways and lungs, helping identify structural abnormalities or signs of inflammation.
- Another essential diagnostic tool for COPD is lung function testing, particularly spirometry, which measures the amount of air an individual can inhale and exhale and how quickly they can do so.
- Spirometry can help assess lung function and detect any airflow obstruction. Additionally, sputum culture tests can be conducted to identify any bacterial or fungal infections contributing to the respiratory symptoms.6
How Is Bronchiectasis Diagnosed?
The best way to accurately diagnose bronchiectasis is using a high-resolution computerized tomography (HRCT) scan. HRCT scans use imaging technology to create 3D models of your lungs by combining images to show their size, shape, and position.7
Because HRCT scans use thinner slices (i.e., detailed views) at higher resolutions to produce 3D models,8 it makes this diagnostic tool particularly useful for examining small structures, like the abnormal widening of the airways and scarring of the tissue.
Bronchiectasis Treatment
Bronchiectasis treatment aims to manage symptoms, prevent infections, and improve overall lung function.
It typically involves a combination of the following:
- Medications
- Airway clearance techniques
- Lifestyle modifications
Your clinician may prescribe antibiotics to treat bacterial infections, while bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids can help alleviate symptoms and reduce airway inflammation.9
In rare cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to remove damaged lung tissue if the disease is affecting a small portion of your lung.10
Airway clearance techniques, such as chest physiotherapy and the use of devices like a positive expiratory pressure (PEP) mask or a high-frequency chest wall oscillation (HFCWO) vest, are crucial in helping individuals with bronchiectasis clear excessive mucus from their airways on a daily basis.11
These techniques can help reduce the risk of respiratory infections to prevent a worsening of symptoms.
Discover a Smart Way to Breathe Easier
How Is COPD Treated?
The management of COPD focuses on relieving symptoms, slowing disease progression, and improving overall quality of life.
- Quitting smoking and avoiding lung irritants are essential steps in managing COPD.
- Medications such as bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and oral medications may be prescribed to reduce symptoms and improve lung function.12
- Pulmonary rehabilitation programs, including exercise training and education, can help individuals with COPD manage their condition and enhance their ability to perform daily activities.13
In severe cases of COPD, surgical interventions like lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplantation may be considered.14 These procedures aim to improve lung function and overall quality of life for individuals with advanced COPD.
Bronchiectasis and COPD: Similarities and Overlapping Symptoms
Despite their differences, bronchiectasis and COPD share some similarities, making it challenging to differentiate between them based solely on symptoms.
As mentioned, both conditions can cause:
- Chronic cough
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
Additionally, individuals with either bronchiectasis or COPD (or a comorbid condition) may experience recurring respiratory infections due to compromised lung function and impaired mucus clearance.
The overlapping symptoms highlight the importance of a thorough medical evaluation and diagnostic tests to differentiate between bronchiectasis and COPD accurately.
Lifestyle Modifications for Bronchiectasis and COPD Symptoms
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle modifications can help individuals manage both bronchiectasis and COPD effectively.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular physical activity and a balanced diet recommended by your clinician, can support overall respiratory health.
- Avoiding exposure to lung irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and chemical fumes is crucial in preventing further damage to the airways and exacerbation of symptoms.
- Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals are necessary to monitor lung function, adjust treatment plans, and address any concerns or new symptoms.
Breathe Easier with SmartVest
Whether you live with bronchiectasis, COPD, or a combination of both conditions, proper diagnosis is crucial to ensure appropriate treatment and management strategies are implemented.
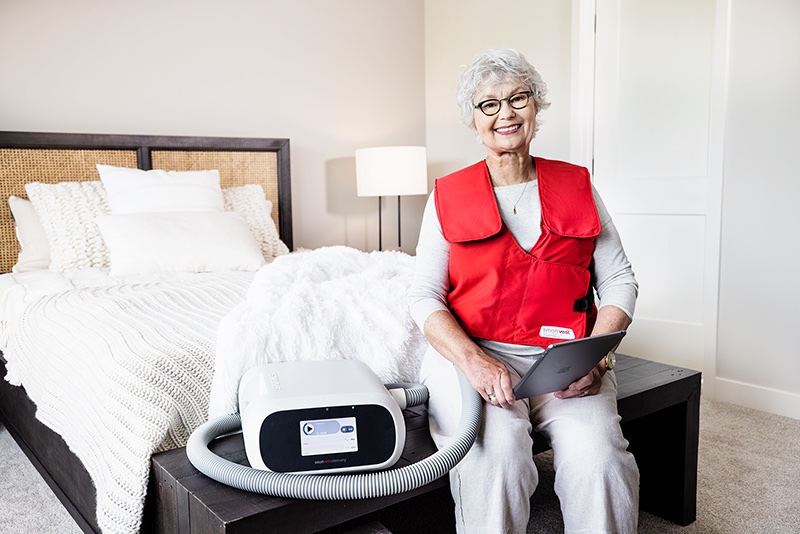
COPD patients diagnosed with a prevalence of bronchiectasis symptoms may be eligible for the SmartVest Airway Clearance System. SmartVest, a HFCWO therapy device, is designed to deliver 360° chest coverage—all with your complete comfort in mind!15
By gently squeezing and releasing the upper chest wall, SmartVest works to loosen, thin, and propel mucus upward where it’s easier to cough up, reducing mucus buildup that leads to infection.16
To determine if you qualify for a SmartVest, contact one of our respiratory experts today! In the meantime, request an information packet to learn more about the life-changing benefits of using airway clearance via SmartVest!
Resources
[1] National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. “What Is Bronchiectasis?” Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/bronchiectasis
[2] Mayo Clinic. “COPD.” Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/copd/symptoms-causes/syc-20353679
[3] National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. “Bronchiectasis: Causes and Risk Factors.” Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/bronchiectasis/causes
[4] American Lung Association. “What Causes COPD.” Retrieved from https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/what-causes-copd
[5] American Lung Association. “Diagnosing COPD.” Retrieved from https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/symptoms-diagnosis/diagnosing
[6] American Lung Association. “Spirometry.” Retrieved from https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-procedures-and-tests/spirometry
[7] National Library of Medicine. “High-resolution CT of the lungs: Indications and diagnosis.” Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29243467/
[8] National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. “Chest CT Scan.” Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/chest-ct-scan
[9] American Lung Association. “Treating and Managing Bronchiectasis.” Retrieved from https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/bronchiectasis/treating-and-managing
[10] Cleveland Clinic. “Bronchiectasis: Management and Treatment.” Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21144-bronchiectasis#management-and-treatment
[11] American Lung Association. “Treating and Managing Bronchiectasis.” Retrieved from https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/bronchiectasis/treating-and-managing
[12] American Lung Association. “Understanding Your COPD Medications.” Retrieved from https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/treating/copd-medications
[13] American Lung Association. “Pulmonary Rehabilitation.” Retrieved from https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-procedures-and-tests/pulmonary-rehab
[14] American Lung Association. “Treating COPD.” Retrieved from https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/treating
[15] Pokorney J. Comparison of Oscillatory Trough Pressure Generated by High Frequency Chest Wall Oscillation (HFCWO) Systems: A White Paper.
[16] Siefert, C. et al. Respiratory Therapy, Vol. 11 No 4, 34-38, 2016.


